Delivering Flexibility Without Complexity
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology products currently under development or being commercialized are specific and personalized in nature. Given this targeted nature the value of these products are high and batch sizes are small. This brings new manufacturing challenges to aseptic fill-finish operations where traditional approaches are not meeting the flexibility, yield or efficiency these products require. To overcome these challenges new flexible solutions are providing manufacturing options for these small batch aseptic filling applications.
One of the most significant technology trends being used for drug product manufacturing today are flexible fill-finish systems that process multiple container options using a common aseptic filling machine. The next generation drug products are more targeted and patient specific by nature causing batch sizes to be much smaller than the traditional mass produced sterile drugs manufactured historically. This paradigm shift paves the way for new solutions that are geared toward manufacturing flexibility. The key to these adaptive aseptic filling technologies is efficient production of high value, high mix (multiple product skews) products irrespective of the final presentation or parenteral container.
With the common goal of maximizing flexibility there are several design approaches now available to industry. These solutions are commonly categorized as follows:
Docking Trolley Filling Machine – This approach uses a flexible isolator that allows dedicated filling machines built onto carts known as “trolleys” to be docked to the isolator. To have the ability to process multiple container formats on the filling line the end user is required to purchase a trolley for each container to be processed. This filling line strategy can provide flexibility however it has the disadvantages of having multiple systems to maintain, store, transfer in and out of the filling suite, additional format parts, and the validation required for each trolley. Reach can sometimes be an issue with this approach because there is access from the front side of the isolator only.
Traditional Matrix Nest Filling Machine – Traditional syringe filling machines with X-Y tables are adapted to process additional nested ready-to-use formats such as vials and cartridges. This type of machine is widely used for syringe filling and closing operation, and is a known and reliable platform. The adaptation of this syringe filling machine to process other formats does introduce its own set of challenges, because by design it was not optimized for vial and cartridge formats. Given the high value nature of the products being processed in-process weighing (IPC) is regularly performed. These systems must remove the containers from the nest, transfer them to weigh cells, weigh the containers, transfer them back to the filling needles to filling and repeat the transfer and weighing process again before placing the containers back into the nest to continue processing. The transferring of containers for this process significantly reduces the overall productivity of the equipment and increase material handling risks.
These systems generally require a significant amount of format parts to enable this solution to process multiple container options. Additional format parts are expensive, add complexity of the system, introduce opportunity for incorrect installation, and require additional parts and surfaces that must be cleaned and / or sterilized prior to manufacturing the subsequent batch.
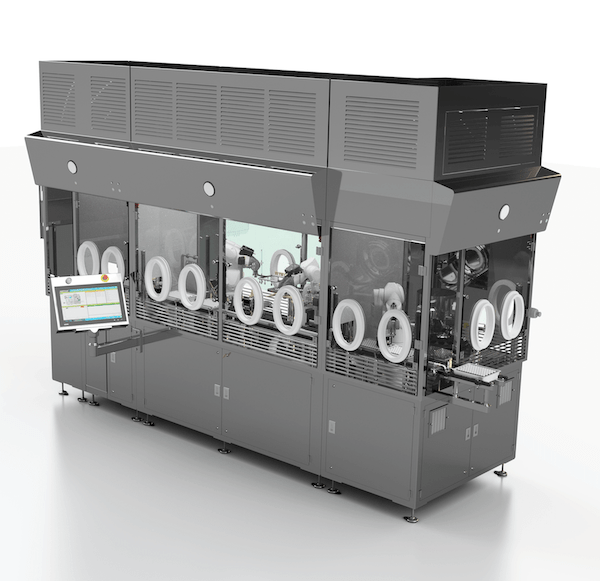
Robotic Adaptive Filling Machine – The integration of robotics into the aseptic filling process is a novel and reliable approach that uses known processes for multiple container formats. This approach uses highly flexible robots that respond to recipe driven inputs by the operator to perform various aseptic processing tasks for filling and closing a variety of container formats including; vials, syringes and cartridges. Adaptive robotic systems are not an evolution of the traditional filling line, but a complete re-think of the overall process to one that designs out the risks and limitations of these older technologies and maintains sound approaches necessary to optimize the production process. These systems provide a modular approach that allows these systems to provide additional operations before and after aseptic filling including; Tyvek lid-liner removal, lyophilization and capping.
AST’s ASEPTiCell is an Robotic Adaptive Filling Machine that provides several advantages that make it the filling line of choice for applications that require multi-format production. ASEPTiCell provides the following key advantages:
- Flexibility comes “baked in” without the need to dock additional machines or trolleys to process various containers.
- Space efficient footprint that minimizes the background cleanroom space required.
- Minimal format parts required to process various container options. The format parts are simple in design and static relying upon the robot for the motion, thereby eliminating common sources of particle generation.
- Recipe driven technology that electronically adapts to the operator recipe inputs without manual adjustments.
- Optimized in-process weighing operation that minimizes container handling and allows for net-weigh filling directly on the load cell.
- Simple design eliminates actuators and mechanisms traditionally used. By eliminating these complex features cleaning, sterilization and bio-decontamination of the line between batches is reduced increasing line utilization and enhancing sterility assurance.
- Processes standard and widely available closures and caps that don’t require nesting.
For commercial and clinical aseptic filling applications, that require flexible manufacturing, AST’s ASEPTiCell provides the optimal processing solution. It’s nimble and unique design approach eliminates key sources of quality risk to provide the simplest solution to producing safe and sterile drug products.

